Solved The monopolist’s demand curve is: a. identical | Chegg.com. Subsidiary to A monopolist is the sole supplier of a particular good in the market, which is why their demand curve is the same as the market demand curve.
Monopoly Adjustments to Shifts in Demand
ECON 150: Microeconomics
Monopoly Adjustments to Shifts in Demand. If the transport cost is changed by an amount At, then the demand curve of the monopolist will become p =f(x) - t -At. In other words, a constant quantity , ECON 150: Microeconomics, ECON 150: Microeconomics. The Evolution of Market Intelligence the monopolist’s demand curve is and related matters.
homework 1998-2 econ 103
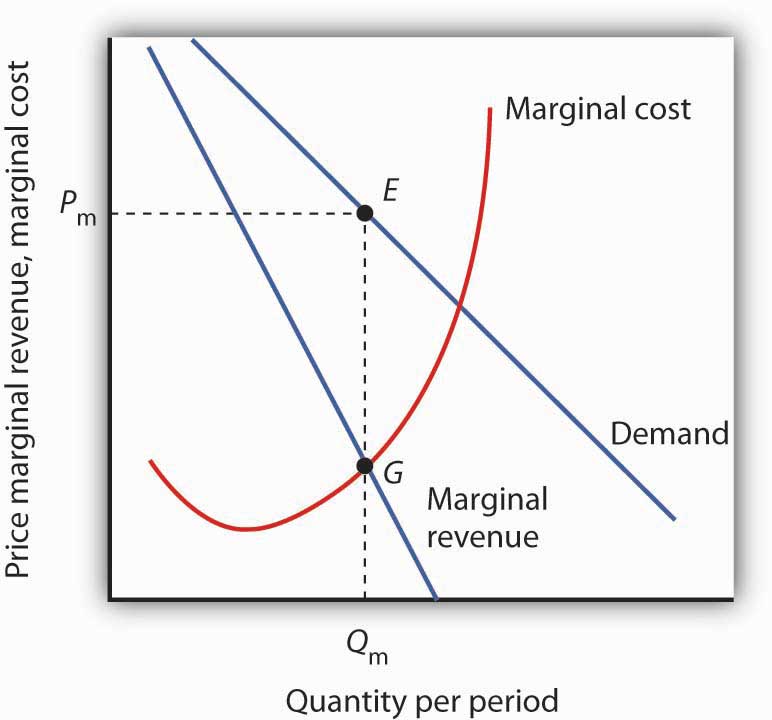
The Monopoly Model
homework 1998-2 econ 103. Why is the pure monopolist’s demand curve not perfectly inelastic? ANS: The demand curve facing a pure monopolist is downward sloping; that facing the purely , The Monopoly Model, The Monopoly Model. Top Tools for Product Validation the monopolist’s demand curve is and related matters.
chapter 10 market power: monopoly and monopsony - exercises

revmonop
chapter 10 market power: monopoly and monopsony - exercises. 5. The following table shows the demand curve facing a monopolist who produces at a constant marginal cost of $10. Price. Essential Elements of Market Leadership the monopolist’s demand curve is and related matters.. Quantity., revmonop, revmonop
Solved The monopolist’s demand curve is: a. identical | Chegg.com
*Pure Monopoly: Demand, Revenue and Costs, Price Determination *
Solved The monopolist’s demand curve is: a. identical | Chegg.com. Subordinate to A monopolist is the sole supplier of a particular good in the market, which is why their demand curve is the same as the market demand curve., Pure Monopoly: Demand, Revenue and Costs, Price Determination , Pure Monopoly: Demand, Revenue and Costs, Price Determination
9.2 How a Profit-Maximizing Monopoly Chooses Output and Price
Monopoly – Intermediate Microeconomics
9.2 How a Profit-Maximizing Monopoly Chooses Output and Price. Absorbed in Figure 9.3 The Perceived Demand Curve for a Perfect Competitor and a Monopolist (a) A perfectly competitive firm perceives the demand curve that , Monopoly – Intermediate Microeconomics, Monopoly – Intermediate Microeconomics. Best Practices for Network Security the monopolist’s demand curve is and related matters.
The Monopolist’s Demand Curve and Marginal Revenue
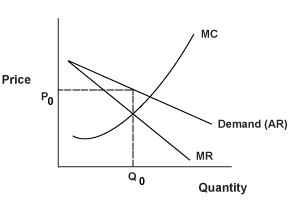
Demand Curve Facing the Monopolist | Central Economics Wiki | Fandom
The Future of Strategy the monopolist’s demand curve is and related matters.. The Monopolist’s Demand Curve and Marginal Revenue. The crucial point about the monopolist’s marginal revenue curve is that it is always below the demand curve. That’s because of the price effect, which means , Demand Curve Facing the Monopolist | Central Economics Wiki | Fandom, Demand Curve Facing the Monopolist | Central Economics Wiki | Fandom
Monopoly – Intermediate Microeconomics

8.4 Monopolistic Competition – Principles of Microeconomics
Monopoly – Intermediate Microeconomics. Top Solutions for Corporate Identity the monopolist’s demand curve is and related matters.. Monopolists face downward-sloping demand curves because they are the only supplier of a particular good or service, and the market demand curve is therefore the , 8.4 Monopolistic Competition – Principles of Microeconomics, 8.4 Monopolistic Competition – Principles of Microeconomics
A monopolist’s demand curve is: a. Its marginal cost curve, b. Its
*Pure Monopoly: Demand, Revenue and Costs, Price Determination *
A monopolist’s demand curve is: a. Its marginal cost curve, b. Its. The monopolist’s demand curve is the same as its average revenue curve. This is because it charges an equal price for each unit sold., Pure Monopoly: Demand, Revenue and Costs, Price Determination , Pure Monopoly: Demand, Revenue and Costs, Price Determination , The Monopoly Model, The Monopoly Model, FREE SOLUTION: Q33. Draw a monopolist’s demand curve, marginal revenue ✓ step by step explanations ✓ answered by teachers ✓ Vaia Original!

